In today's digital age, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. However, researchers are increasingly interested in understanding how our online habits may be affecting our mental wellbeing and cognitive abilities. A recent study delves into the complex relationships between objective social media use, attentional control, and psychological distress.
The study aimed to explore how the amount of time spent on social media platforms correlates with an individual's ability to focus and their overall mental health. Unlike previous research that relied heavily on self-reported data, this investigation utilized objective measures of social media usage, providing a more accurate picture of participants' online behaviors.
Researchers tracked participants' social media activity through specialized software, measuring factors such as time spent scrolling, frequency of app opens, and engagement with content. This data was then analyzed alongside assessments of attentional control and psychological distress.
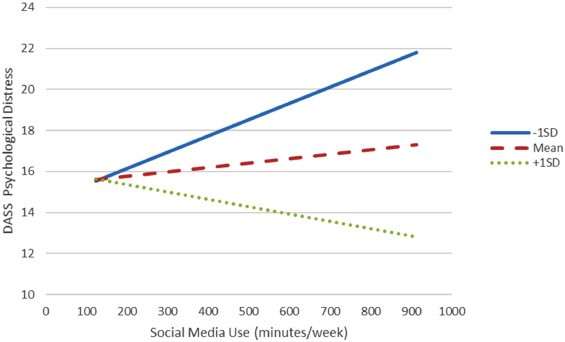
The findings suggest a nuanced relationship between social media use and mental health. While excessive use was associated with higher levels of psychological distress, moderate usage showed no significant negative effects. Interestingly, the study revealed that individuals with better attentional control were less likely to experience negative psychological outcomes from social media use.
These results highlight the importance of developing strong attentional control skills in our increasingly connected world. The ability to focus and resist distractions may serve as a protective factor against the potential negative impacts of social media on mental health.
The study's authors emphasize that social media itself is not inherently harmful. Rather, it's how we engage with these platforms that can influence our wellbeing. They suggest that future research should focus on developing strategies to help individuals use social media more mindfully and productively.
As we continue to navigate the digital landscape, understanding the complex interplay between our online behaviors and mental health becomes increasingly important. This research provides valuable insights that can inform both individual usage habits and broader public health strategies related to social media consumption.
By shedding light on the links between social media use, attention, and psychological distress, this study paves the way for more targeted interventions and education programs. It underscores the need for a balanced approach to social media use, one that acknowledges both its benefits and potential pitfalls.
As our digital lives continue to evolve, so too must our understanding of how these technologies impact our cognitive abilities and mental health. This research represents an important step forward in that ongoing journey of discovery.