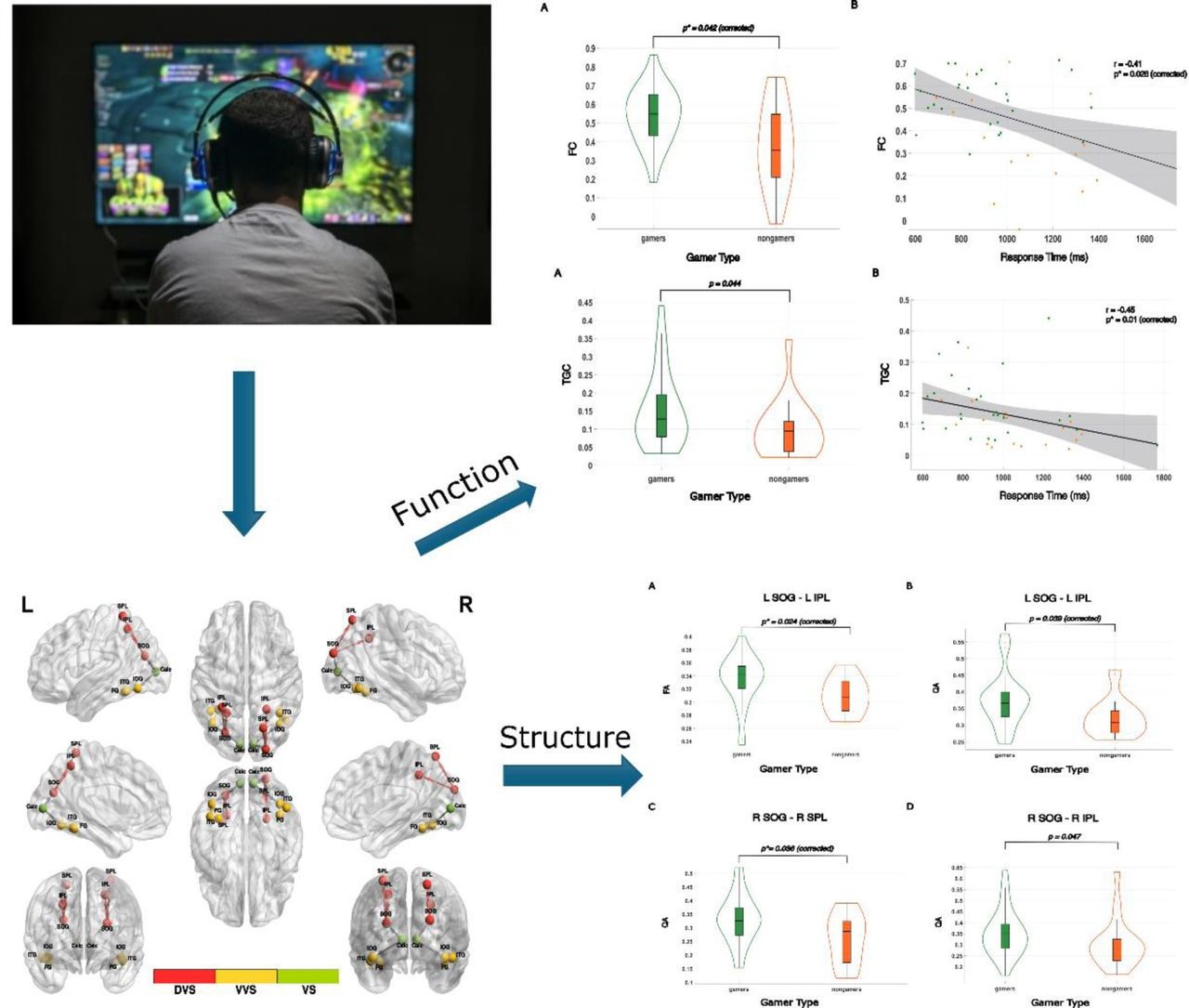
Action Gaming Rewires Brain's Visual Processing Networks
New research reveals that action gamers develop enhanced brain connections for processing visual information, particularly in regions handling spatial awareness and movement. The study found stronger neural pathways in gamers' dorsal visual streams, potentially explaining their superior performance in visual decision-making tasks.
Infants Show Remarkable Self-Awareness: Three-Month-Olds Can Detect Their Own Heartbeat
Groundbreaking research reveals that babies as young as three months can perceive their own heartbeat, challenging previous assumptions about early human development. Using innovative eye-tracking technology, researchers discovered infants pay more attention to animations synchronized with their internal body rhythms.
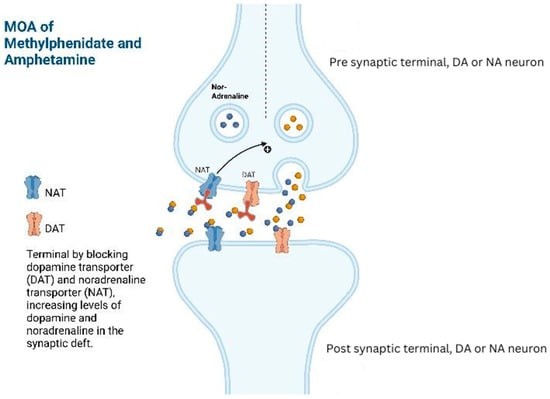
Limited Memory Benefits Found in ADHD Medication Study of Healthy Adults
New research challenges claims about cognitive enhancement from ADHD drugs, finding that low doses of methylphenidate only modestly improved numeric memory in healthy adults. The Swinburne University study reveals no broad cognitive benefits, raising concerns about the medication's widespread use as a 'smart drug'.
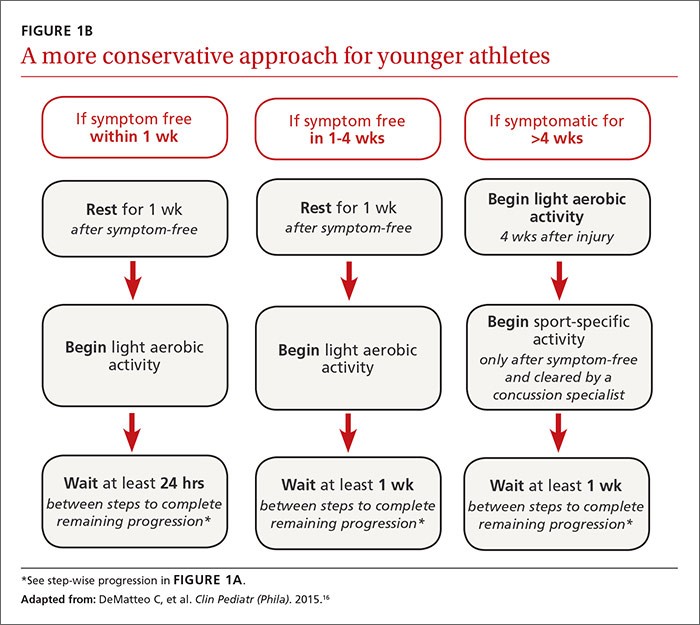
Early Concussions Cast Long Shadow Over Academic Future, Finnish Study Finds
Research from the University of Tampere reveals children with mild concussions are 15% less likely to pursue higher education compared to those with non-head injuries. The groundbreaking study of 24,000 patients demonstrates how early brain trauma can have lasting effects on educational achievement well into adulthood.
Brain and AI Speak the Same Language: New Study Reveals Striking Similarities in Neural Processing
Groundbreaking research by Google and leading universities uncovers remarkable parallels between how Large Language Models and human brains process language. The study demonstrates linear alignment between neural activity patterns and AI embeddings during speech comprehension and production.
Age Impacts How Children with Social Anxiety Process Mistakes, Study Finds
New research reveals younger children with social anxiety struggle more to refocus after making mistakes compared to older children with the same condition. The study of 214 children shows this deficit diminishes around ages 11-13, suggesting developmental changes help overcome initial processing challenges.
Primary School Children Show Superior Ability in Understanding Cause and Effect
A groundbreaking study reveals that primary school children outperform both younger and older age groups in associative learning abilities. The research challenges previous assumptions and provides valuable insights into age-specific learning patterns that could inform educational approaches.
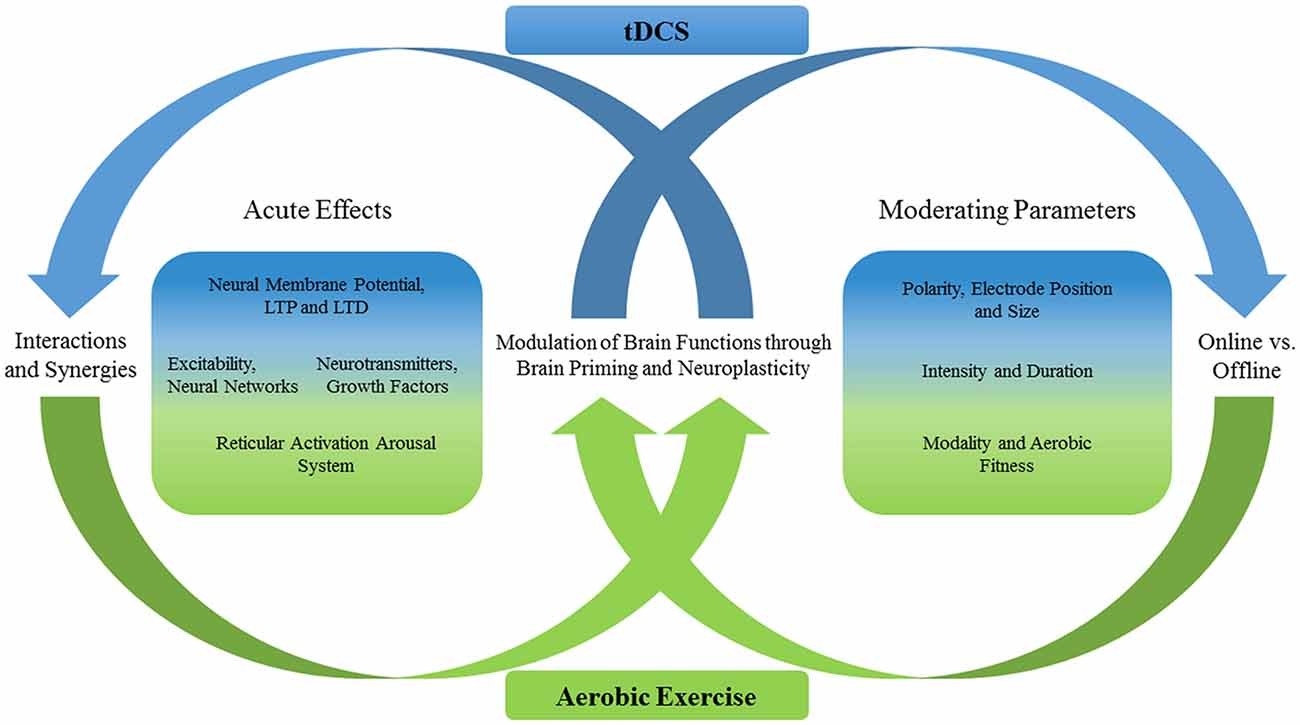
Exercise Boosts Brain Function Differently in Adults with ADHD, Study Finds
New research from Taiwan reveals that 30 minutes of aerobic exercise enhances cognitive performance specifically in adults with ADHD through unique brain activity patterns. The groundbreaking study demonstrates how physical activity affects brain function differently between ADHD and non-ADHD individuals.
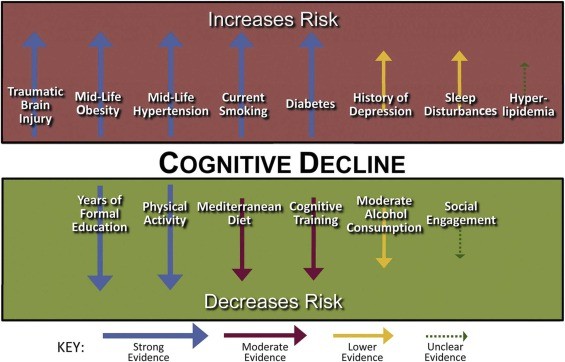
Digital Lifestyle Program Shows Promise in Delaying Dementia Onset
A groundbreaking Australian study reveals that an online lifestyle intervention program can enhance cognitive function in older adults at risk of dementia. The three-year trial demonstrated that personalized digital coaching focusing on exercise, diet, brain training, and mental health could potentially delay dementia onset by one year.
Hidden ADHD: How Excessive Daydreaming Delays Adult Diagnosis
New research reveals that maladaptive daydreaming could mask symptoms of ADHD in adults, leading to delayed diagnosis. The study found that adults diagnosed later in life exhibited higher levels of compulsive fantasizing that interfered with recognizing underlying attention deficit symptoms.