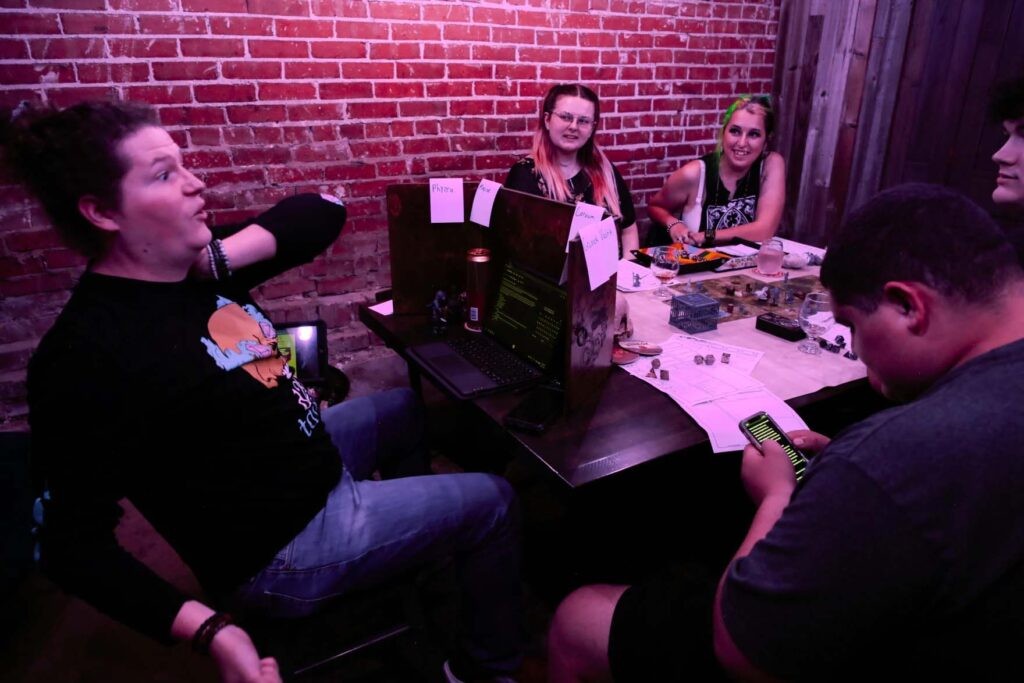
Dungeons & Dragons: A Therapeutic Path from Gaming Addiction to Social Connection
A groundbreaking study reveals that tabletop role-playing games like Dungeons & Dragons may help reduce gaming addiction and social anxiety symptoms. The 10-week program showed promising results with decreased loneliness and problematic gaming behaviors among participants.
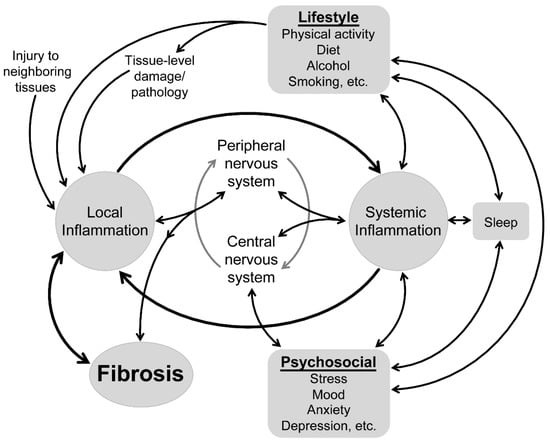
Inflammation Link Discovered in Treatment-Resistant Depression: New Hope for Patients
Groundbreaking research from the University of Queensland reveals how inflammation and metabolic dysfunction may impair dopamine production in treatment-resistant depression. The findings suggest potential new treatment approaches and the development of blood tests to predict antidepressant response.
Social Media Detox Myth: New Study Finds No Mental Health Benefits from Digital Breaks
A groundbreaking meta-analysis of over 4,600 participants reveals that temporary social media breaks do not improve mental wellbeing or life satisfaction. The Belgian research challenges popular 'digital detox' claims, suggesting more nuanced approaches to healthy social media use may be needed.
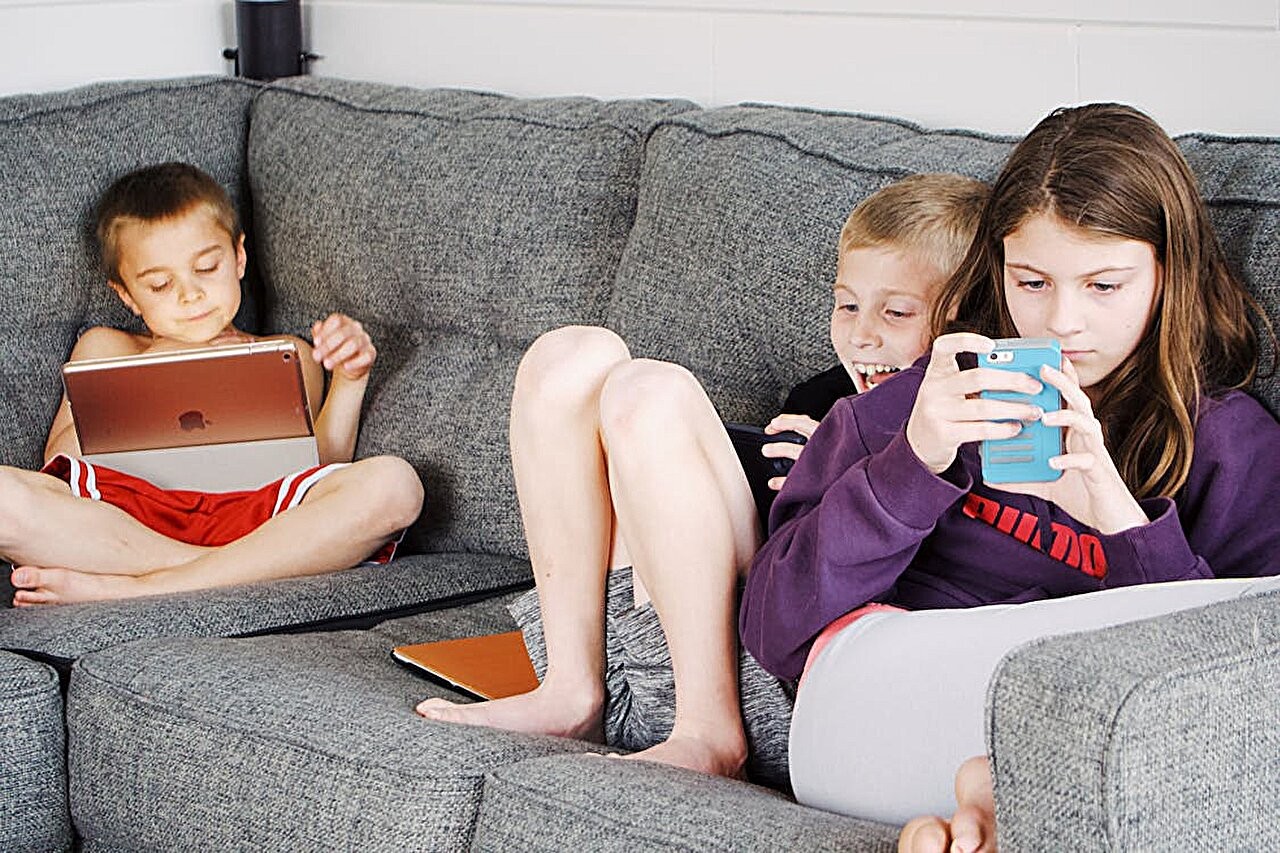
Screen Time and Mental Health: New Study Reveals Hidden Risks for Teens
Research shows teenagers spending over three hours daily on sedentary activities face increased psychological distress risks, with video gaming and excessive leisure reading as key concerns. The groundbreaking study tracked 3,675 adolescents, revealing nuanced impacts of different types of screen time on mental wellbeing.
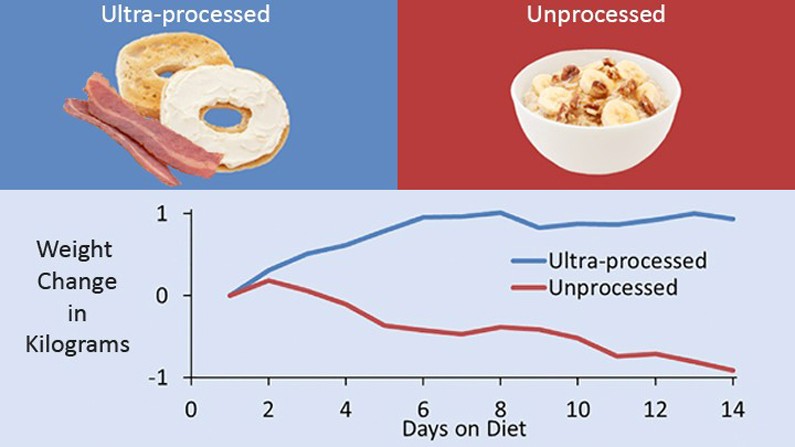
Cutting Ultra-Processed Foods in Half Shows Dramatic Health and Mood Benefits
A groundbreaking Drexel University study reveals that halving ultra-processed food consumption leads to significant weight loss and improved mood in just eight weeks. Participants lost an average of 7.7 pounds while reducing calories, sugar, and saturated fat through a comprehensive intervention program.
Screen Time in Early Years Linked to Teen Mental Health Crisis
An eight-year Finnish study reveals troubling connections between childhood screen time and adolescent psychological issues. Research shows children with higher device usage face increased rates of depression and stress as teenagers, highlighting the need for balanced digital environments.
Digital Detox Experiment Reveals Dramatic Mental Health and Cognitive Benefits
A groundbreaking study shows that taking a two-week break from mobile internet access led to improved mental well-being and cognitive function in 91% of participants. The research suggests humans are not adapted to constant connectivity, with benefits including better sleep, stronger social connections, and attention span improvements.
Physical Exercise Emerges as Promising Treatment for Internet Addiction
A groundbreaking Chinese study reveals that regular exercise could effectively combat Internet addiction while enhancing mental wellbeing. Research involving 760 college students showed significant improvements in managing Internet use and reducing anxiety through structured physical activity programs.